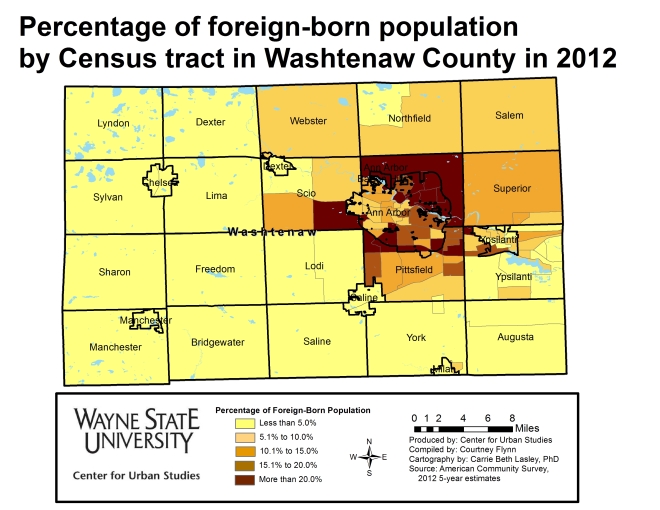
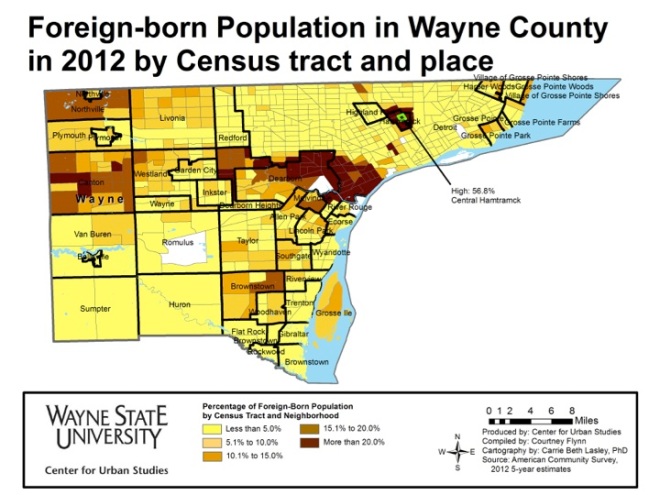
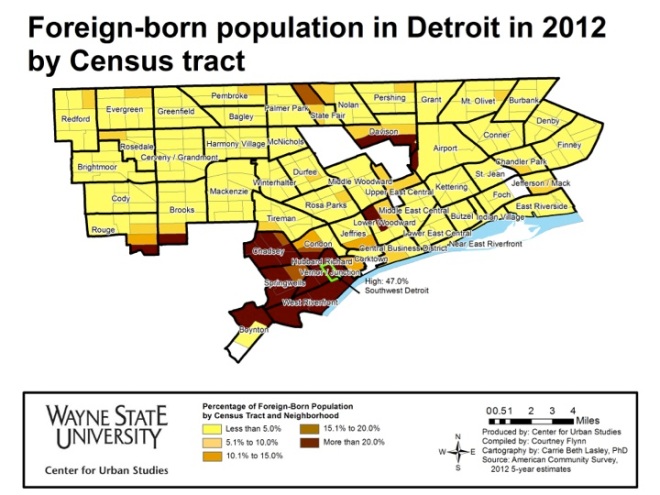
In recent weeks news has broken about outbreaks of diseases many have thought were eradicated. From a mumps outbreak in the NHL to a measles outbreak at Disney World, in which the pattern includes seven different states with a whooping cough outbreaks, and a measles outbreak much closer to home in Grand Traverse and Leelanau counties- we are seeing that these diseases are indeed making a comeback, and many believe it is because of the growing number of children not being immunized.
While there have been no such outbreaks as mentioned above, immunization rates do vary in Southeastern Michigan, with some school districts having rates lower than the minimum thresholds needed to prevent the spread of disease. This is problematic, as low immunization rates threaten herd immunity and puts both vaccinated and non-vaccinated individuals at risk.
What is herd immunity?
The phrase “herd immunity” refers to protecting a community from disease by having a critical mass of its population immunized. Rather than just protecting the person vaccinated, vaccines can protect the entire community by breaking the chain of an infection’s transmission. However, for this to be successful, a certain number of people have to be vaccinated.
Epidemiologists have determined a basic threshold for infectious disease transmission by calculating both a “basic reproduction number” (R0), which represents how many people in an unprotected population one infected person can pass the disease along to – basically, a single person with mumps can pass it along to between 4 and 7 non-vaccinated people, while a single person with the measles could pass it along to between 12 and 18. The higher this R0 value is, the higher the percentage of vaccinated people in the population has to be, in order to prevent the spread of these illnesses. Therefore, in order to prevent an outbreak of measles, for instance, in a school district, 89-94% of students would have to be immunized.
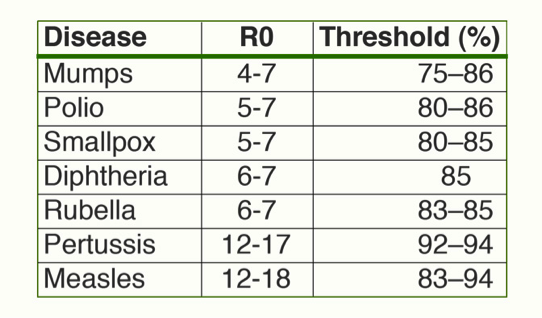
Photo credit © Tangled Bank Studios; data from Epidemiologic Reviews, 1993.
Furthermore, it is important for the population to be immunized in order to protect the health of those who cannot be vaccinated, such as infants and people with weakened immune systems. When large chunks of the community are not protected against these diseases, it is these groups of people whose health with be the most affected.
What are the immunization rates in Southeast Michigan schools?
Rates vary from well above minimum threshold numbers for even the most contagious diseases (Hazel Park and Southfield schools both have rates of 98%) to far below the threshold for any sort of protection (Madison Public Schools has the lowest, at only 70% vaccinated). However, it is important to note that not all school districts track vaccination rates uniformly – Inkster Public Schools, for instance, is reporting a 100% vaccination rate, but that’s based on an interview with a very small sample of students and may not be accurate.

Note: Data unavailable for Willow Run Schools (white area), as it was absorbed into Ypsilanti Schools this year.
One interesting trend present in the map is how more affluent districts seem to have lower vaccination rates than their less affluent counterparts, suggesting that non-vaccination is more of a trend in middle- to upper-income communities (although this certainly does not hold true for all). One important fact about herd immunity is that being vaccinated yourself (or vaccinating your children) matters less when the population isn’t immunized. For example, an unvaccinated student in Hazel Park would have less of a chance of catching a vaccine-preventable illness than a vaccinated student in neighboring Madison Heights, since it would be exceedingly difficult for disease to spread in a population that is nearly universally protected against it.
What is Michigan doing to boost vaccination rates?
As of January 1, 2015, the Michigan Department of Community Health changed their rules on obtaining an exemption waiver for vaccinations. Starting this year, parents will still have the right to refuse inoculations, but first they have to be educated by a local health worker about vaccines and the diseases they are intended to prevent, and sign a universal state form that includes a statement of acknowledgement that they understand they may be putting their own children and others at risk by refusing shots.
Currently, Michigan is one of 20 states that allow such an exemption. With this being the case, it was still easier to obtain a waiver here than it is elsewhere – for instance, Arkansas and Minnesota require a waiver form to be notarized, and Vermont requires parents who opt out to renew their waiver each year, instead of just for kindergarten, sixth grade, and in the event of a school transfer.
There is a definite correlation between the ease of getting an exemption waiver for vaccinations and the percentage of students who obtain waivers, as one study (Blank, Caplan & Constable, 2013) found that states with an easier process had waiver rates twice as high as those with more complicated ones. Therefore, by tightening these restrictions, Michigan’s vaccination waiver rates may decrease, and vaccination rates may increase.
Sources
http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/body/herd-immunity.html
http://www.mlive.com/news/index.ssf/2014/12/vaccination_rule_change_propos.html
Blank, N.R., Caplan, A.R. & Constable, C. (2013) Excempting schoolchildren from immunizations: States with few barriers had highest rates of nonmedical exemptions. Health Affairs 32(7): 1282-1290. http://content.healthaffairs.org/content/32/7/1282.abstract